
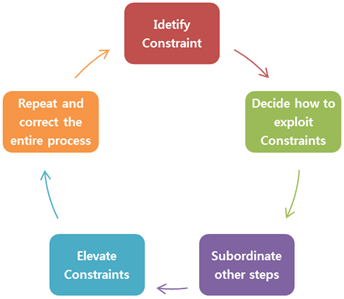
Elevate the system’s constraints: Look at opportunities of eliminating the constraint from the value flow.Subordinate all the other steps in the process to the above decision (Step 2): Modify and make changes to the upstream and downstream processes to be aligned with the pace of the constraint.Exploit & Explore the constraints to maximize the Throughput: Brainstorm and identify quick improvement steps that will help the system to keep running without any stoppages due to the constraint.Identify the constraints influencing Throughput: Identify the current constraint which is a single step in the entire process flow that limits the rate of achieving goal.A five step approach for constraint management is described below: Policy Constraint: The policies and processes set by the organization may sometimes hinder or act against the throughput maximization.Ī system can achieve maximum throughput by managing its constraints.People Constraint: Availability of skilled manpower and high manpower cost are some examples of People constraint.Equipment Constraint: Availability of equipment, working hours of a machinery, efficiency and maintenance requirement are some of equipment constraint.
Physical Constraint: Availability of materials, lack of physical space is some of the examples of physical constraint.There are various types of constraints that impact the rate of output (throughput). So, the organization should focus on discovering and removing or reducing the impact of it on throughput. Internal constraint is when the system delivers less than the market demand. In such a case, organization should create demand for the product in market. External constraints are when the system can produce more than what the market demands. Types of ConstraintsĬonstraints can be external or internal. A constraint is a roadblock that prevents the process from achieving the throughput even when nothing goes wrong. Any system has at least one constraint which it has to tackle and survive in business.Ĭonstraints should not be confused with short term interruptions like breakdown, employee absenteeism etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
